Table of Contents: What You Will Read
What is Polypropylene?
Polypropylene (pp), or polypropene, is a synthetic, man-made material classified as plastic within the polyolefin group of hydrocarbon polymers and plastic products similar to polyethylene. Polypropylene (abbreviated PP) is a highly versatile plastic known to be used as a fibrous, structural or textile-type material within an extensive collection of industry applications and modern items. It has a high melting point, exceptional durability and good chemical resistance, making it suitable for a broad range of applications.
How is Polypropylene Made?
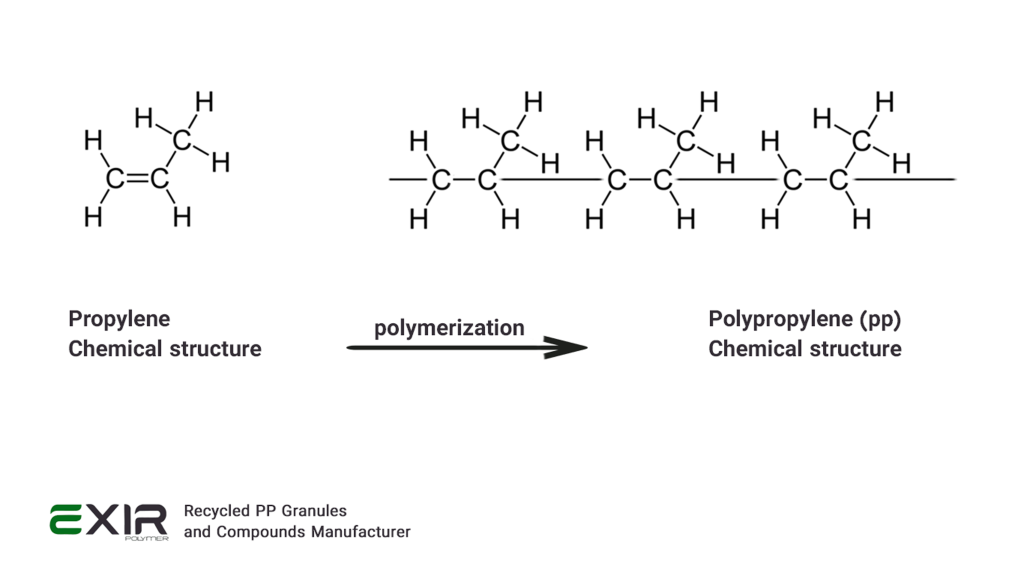
Polymerization is the technique used to create polypropylene plastic. First, the monomer propylene must be obtained; this can be done by using natural gas or fossil fuels. After the propylene monomer is extracted, it goes through a chemical process called polymerization, in which the monomer molecules join forces to create lengthy PP chains.
Various techniques can be employed to polymerize propylene, contingent upon the intended characteristics and uses of the resulting PP. Ziegler-Natta catalysts, coordination complexes that speed up the polymerization process, are one popular method. These catalysts aid in regulating the resultant polypropylene’s molecular weight and structure.
A different option for polymerization is to use metallocene catalysts. In order to produce polypropene with certain qualities like increased heat resistance or transparency, metallocene catalysts provide more exact control over the polymer structure.
The manufacturing of PP can also be done by high-pressure methods. In order to accelerate the polymerization reaction, propylene monomer is subjected to high pressures and temperatures throughout these operations.
The tacticity (side group arrangement) and other qualities needed for the intended use of PP, as well as the necessary molecular weight, all influence the choice of polymerization technique. All of these techniques have unique benefits and may be customized to suit certain production demands.
Polypropylene Structure and Chemical Compound

Since polypropylene is a linear polymer, its polymer chains are arranged in a systematic manner. This indicates that there is a straight and organized alignment of the chains. (C3H6)n, where “n” indicates the number of units that repeat in the polymer chain, is the chemical formula for polypropene. Atoms of hydrogen and carbon make up the majority of the structure of PP. The foundation of the polymer chain, which is made up of carbon atoms, gives the material strength and stability. Because of its structural makeup, polypropene is thermoplastic—it can be melted and treated again without significantly losing its original qualities. Because of this property, polypropylene is very adaptable and good for a range of production and recycling techniques.
What Are the Properties of Polypropylene?
PP has a wide range of properties that contribute to its popularity in various applications in the industry:
Mechanical Properties
Due to its remarkable mechanical qualities, polypropylene is applied in a broad range of applications. Because of its high tensile strength, it can withstand heavy pulling forces without breaking or buckling. Additionally, polypropene is very rigid, allowing it to retain its structural integrity when subjected to external stresses. It is appropriate for applications where impact or shock absorption is critical due to its remarkable impact resistance, which enables it to absorb and distribute energy. Furthermore, polypropylene’s resilience and durability in applications that need long-term structural and performance robustness are guaranteed by its capacity to bear repeated flexing and bending without breaking.
Thermal Properties
Due to its superior thermal qualities, polypropene may be used in situations where it will be exposed to high temperatures. PP is a thermosetting material that can tolerate high temperatures without experiencing considerable deformation or loss of structural integrity. Its melting point ranges from 130°C to 171°C, depending on the grade. Additionally, it has exceptional heat resistance, holding onto its physical characteristics even after prolonged exposure to heat. Furthermore, polypropylene has a low coefficient of thermal expansion, which actually means that when it is exposed to temperature changes, its dimensions hardly change. This feature ensures dimensional reliability and stability in situations where temperature fluctuations occur.
Chemical Properties
Because of its exceptional chemical resistance, polypropylene may be applied in a broad variety of applications. It can function properly in harsh chemical settings due to its tolerance to a wide range of acids, solvents and bases. Furthermore, polypropene cannot be affected by water, which adds to its resilience in humid or damp environments. It is crucial to remember that PP plastic may deteriorate when exposed to certain substances, such as strong oxidizers or aromatic hydrocarbons. Consequently, when choosing polypropylene plastic for applications involving exposure to such substances, careful consideration of chemical compatibility is essential.
Polypropylene Uses
Polypropylene can be greatly used in various industries because of its chemical resistance, weldability, versatility and other desirable properties. Some common applications of polypropene include:
Automotive
In the automobile sector, PP is widely used, especially for different parts such as dashboards, battery casings, interior trims, and bumpers. Because of its lightweight design, cars are able to weigh less overall, which improves fuel economy and lowers pollutants. Moreover, polypropylene’s remarkable chemical resistance allows it to tolerate exposure to a variety of vehicle fluids and chemicals, guaranteeing the components’ lifetime and durability. Its resistance to high temperatures further makes it ideal for use in engine compartments and other locations where temperatures are likely to be high.
Packaging
Food containers, plastic bags, and bottles are just a few of the many packaging products made from polypropylene. Because of its remarkable clarity, products may be presented in an aesthetically pleasing manner that increases exposure. Additionally, the minimal moisture absorption of polypropene guarantees that packaged items stay safe and unaffected by harm caused by moisture. Its strong impact resistance also offers durability and protects objects during handling and transit. Polypropylene’s adaptability makes it the perfect material to package a wide variety of goods, guaranteeing their preservation and upholding product quality.
Electrical and Electronics
Because of its superior electrical insulating qualities, PP plastic has extensive usage in electrical and electronic applications. It functions as a dependable cable insulation material, offering strong defense against leakage of electrical current and preserving signal integrity. Additionally, polypropylene plastic is frequently used in capacitors, where it facilitates the effective storage and release of electrical energy. It is also used as a battery separator, guaranteeing the secure and effective operation of batteries. Polypropene is a useful material for a variety of electronic components due to its electrical insulating properties, which support the dependable and effective operation of electrical systems.
Medical
With applications in many vital sectors, polypropylene is a substance that is used extensively in the medical industry. Surgical tools, medical packaging, and disposable syringes are among the products made using them because of their remarkable qualities. As polypropene is highly biocompatible, there is less chance of negative responses and the material will be compatible with the human body. It is also easily sterilizable by employing standard techniques like autoclaving, which guarantees the sterility and safety of medical equipment. Along with durability and maintaining the integrity of medical products, PP’s resistance to chemicals frequently employed in healthcare settings further enhances its appropriateness for medical applications.
Textiles
In the textile business, PP fibers are used in many different applications, most notably in the manufacturing of non-woven fabrics, carpets, furniture, and geotextiles. These polypropene fibers are perfect for usage in a variety of contexts because of their remarkable resistance to mildew, moisture, and stains. Polypropylene fabrics offer dependable endurance and durability for both indoor and outdoor applications, continuing to function well even under harsh conditions. Polypropene fibers are a popular choice because of their inherent qualities, which ensure that the final fabrics can endure wear and tear while maintaining their aesthetic appeal.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Propylene?
Here are some of the main advantages and disadvantages of this amazing material:
Advantages
- Versatility: With a broad spectrum of qualities that make it appropriate for a variety of applications, polypropylene plastic is very adaptable. Its adaptability is enhanced by its flexibility as well as being resistant against toxins.
- Lightweight: Because of its low weight, PP is a useful material in situations where a reduction in weight is sought. Because of its low density, it may be used in aircraft and automobile applications, which helps to increase fuel economy.
- Cost-effective: When compared to other technical polymers, this material is comparatively affordable. It is a popular option for many applications due to its cost, particularly in sectors that need huge amounts of plastic materials.
- Recyclability: Polypropene may be recycled by melting it down and using the melted material to create new products. This lowers waste and encourages sustainability.
Disadvantages
- Limited temperature resistance: Although it has a decent level of heat resistance, this material is not as heat resistant as certain other technical polymers. Its utility in applications exposed to intense heat is limited by its tendency to soften or distort at high temperatures.
- Susceptible to UV degradation: UV light may degrade and discolor this material if it is exposed to it for an extended period of time. Additives or coatings are frequently applied to improve the material’s UV resistance in outdoor applications in order to reduce this.
- Flammability: One combustible substance that ignites readily is PP plastic. Nevertheless, in some applications, flame-retardant chemicals can be added to improve fire resistance.
- Poor bonding properties: Because polypropene has a low surface energy, it is difficult for it to stick or connect to other materials. To create solid and long-lasting bonding, certain surface treatments or adhesives could be needed.
The Different Types of Polypropylene
Polypropylene is available in different types and grades to suit different application needs. Two of its most common types are explained below:
Homopolymer
The process of polymerization, which entails the interaction of propylene monomers with a catalyst at high temperature and pressure, yields polypropylene homopolymer, a thermoplastic substance. Propylene is the only monomer unit that makes up this homopolymer.
Because of its high melting point, rigidity, and superior chemical resistance, polypropylene may be used in a variety of severe settings. It also offers great impact strength, minimal moisture absorption, and outstanding electrical characteristics. It’s a transparent substance that machines, extrudes, and molds readily. It also costs less than comparable technical polymers, which makes it a more appealing choice for producers.
Many sectors, including consumer products, automotive, packaging, medical equipment, and food containers, employ homopolymer extensively. Excellent chemical resistance and the ability to tolerate corrosive chemicals make it the perfect material for tanks, pipelines, and laboratory equipment. It is appropriate for precision items like gears and bearings due to its strong dimensional stability. Fibers, films and sheets for apparel, carpets, and protective packaging are also made from it. Films and sheets made of homopolymer have outstanding clarity and minimal haze, while the fibers themselves are strong and resistant to moisture.
Copolymer
Thermoplastic polypropylene copolymer is created when propylene and ethylene monomers are copolymerized with a catalyst in particular circumstances. The final product has a molecular structure that includes both propylene and ethylene monomer units. This is the distinction between copolymer and homopolymer polypropylene.
PP plastic is the material of choice for things that need to be durable and lightweight because of its great chemical resistance, strong impact strength, and comparatively low density. Its superior fatigue resistance makes it ideal for use in products that are subjected to repeated stress. Because it also has a high gloss finish and superb transparency, it is commonly utilized for consumer goods.
Packaging, home goods, vehicle components, textile manufacturing, and medical equipment are among the many products that employ polypropene. It is also used by the textile industry to make nonwoven fabrics for filters and protective gear.
Conclusion
Polypropylene is used in a wide range of sectors, with the packaging sector being its primary user, because of its flexibility, durability, chemical resistance and other advantageous qualities. While this BPA-free thermoplastic polymer is thought to offer no health risks to humans, prolonged exposure to UV light or very high temperatures may cause it to break down or even leak chemicals. Although there are other molding techniques used in the production of plastics, injection molding is the method most often used to process this material.


 فارسی
فارسی العربية
العربية